Graylog2 - 2 - logstash input http
Introduction
- Configure GELF input in graylog.
- Prepare logstash to input data from any http post.
- Send data to GELF input in graylog using plugins_output_gelf.

Requirements Ansible
As explained in Generic-help installing roles. And at Graylog_ansible_installing_roles
We will use requirements.yml to add this:
- src: mrlesmithjr.logstash
name: ansible-logstash
version: master
Then install with ansible-galaxy install -r requirements.yml
It will install the role with name ansible-logstash, we will use that name in our playbook.
Requirements Graylog2
Here we need to add an input to receive the messages from logstash.
- Select GELF UDP INPUT.
- We will use port 12201
- save
- Start the input
After done, you could see something like:
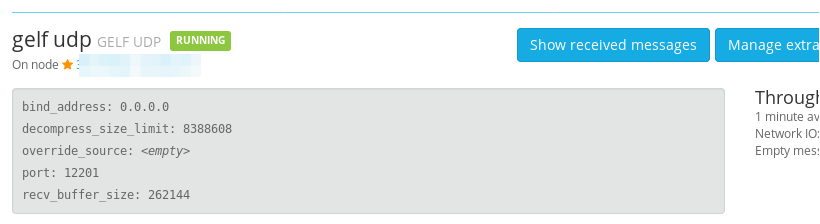
Port below 1024 will not work
Graylog2 is running as normal user, linux will not allow port below 1024
Ansible Inventory
We will use same inventory as created at: at Graylog_ansible_inventory
Preparing the playbook to run the roles
Here we will add to roles.graylog2.yml as examplained at: Graylog_ansible_playbook
- name: Apply logstash for graylog2 servers
hosts: graylog2_servers
become: yes
roles:
- role: ansible-logstash
tags:
- role::logstash
- graylog2_servers
Preparing the variables
We will create new file group_vars/graylog2_servers/logstash_vars
The folder was created during the preparatives at: Graylog_ansible_variables
Variables:
# logstash role:
pri_domain_name: 'example.com'
config_logstash: True
logstash_install_java: false
# These are the files that will be used and will be created in `/etc/logstash/conf.d/`
logstash_base_configs:
- '000_inputs'
- '001_filters'
- '999_outputs'
# Plugins required by us
logstash_plugins:
- 'logstash-output-nagios_nsca'
- 'logstash-output-gelf'
# see https://github.com/mrlesmithjr/ansible-logstash
logstash_base_file_inputs: []
# We don't need it really, but will add anyway
logstash_base_inputs: #define inputs below to configure
- prot: 'tcp'
port: '10514' #gets around port < 1024 (Note...Configure clients to send to 10514 instead of default 514)
type: 'syslog'
# Here we are creating one input, in this case we will add a tag to make it easier to filter
# example is with azure tag, but can be any other.
logstash_custom_inputs:
- input: 'http'
lines:
- 'port => "51202"'
- 'type => "http"'
- 'tags => "azure"'
# Here we will use the tag to create a filter and apply json module to
# transform the message into json format
logstash_custom_filters:
- lines:
- 'if "azure" in [tags] {'
- ' json {'
- ' source => "message"'
- ' }'
- '}'
# As we will not use any default output, we will leave it as empty list []
logstash_base_outputs: []
# Here we will tell ansible role to configure the output to our GELF UDP input.
logstash_custom_outputs:
- output: 'gelf'
lines:
- 'host => "localhost"'
- 'port => "12201"'
All these vars will tell what we exactly want from ansible role for logstash.
Run the playbook
use same steps as described in: Graylog_ansible_run
Or run only logstash role calling with tag:
ansible-playbook -i inventory roles.graylog2.yml --limit graylog2_servers -u user -k -K --become --tags role::logstash
Test your logstash http input
Test command:
curl -XPOST http://yourhost:51202/ -p0 -d '{"status": "Activated", "host":"portal.azure.com", "context": {"portalLink": "https://portal.azure.com/#resource/subscriptions/s1/resourceGroups/useast/providers/microsoft.foo/sites/mysite1"},"facility":"test", "_foo":"bar"}'
Upgrading logstash
Just use normal package upgrade from your distribution.
Receive Azure alarms
Just setup your azure alarms,
to your public IP and HTTP Port: 51201 as done at Preparing the variables